What issues do children with ENT conditions face?
VULNERABLE HEALTH & FREQUENT INFECTIONS
Children are more prone to infections and frequent illness.
COMMUNICATION CHALLENGES
ENT conditions can cause speech delays which hinder a child’s ability to communicate, preventing them from connecting with others.
STIGMA
Children often experience discrimination, leading to poor self-confidence and isolation.
How does surgery change a child’s life?
- As hearing improves, speech improves, restoring confidence as children participate in community life.
- As sleep disordered breathing or obstructive sleep apnea improves, snoring, breathing, and sleep disturbance improve, restoring good feeding and growth.
- A child’s life can be saved as airway obstruction improves.
Learn more about Endoscopic surgery here.
Conditions We Treat
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media is defined as a persistent or intermittent infection or pus discharge through a torn ear drum. Common symptoms include painless ear discharge and hearing loss. Lack of timely treatment can result in complications like meningitis, brain abscess, hydrocephalus, sigmoid sinus thrombosis, facial nerve palsy, and mastoid abscess. The treatment is both medical and surgical therapy.
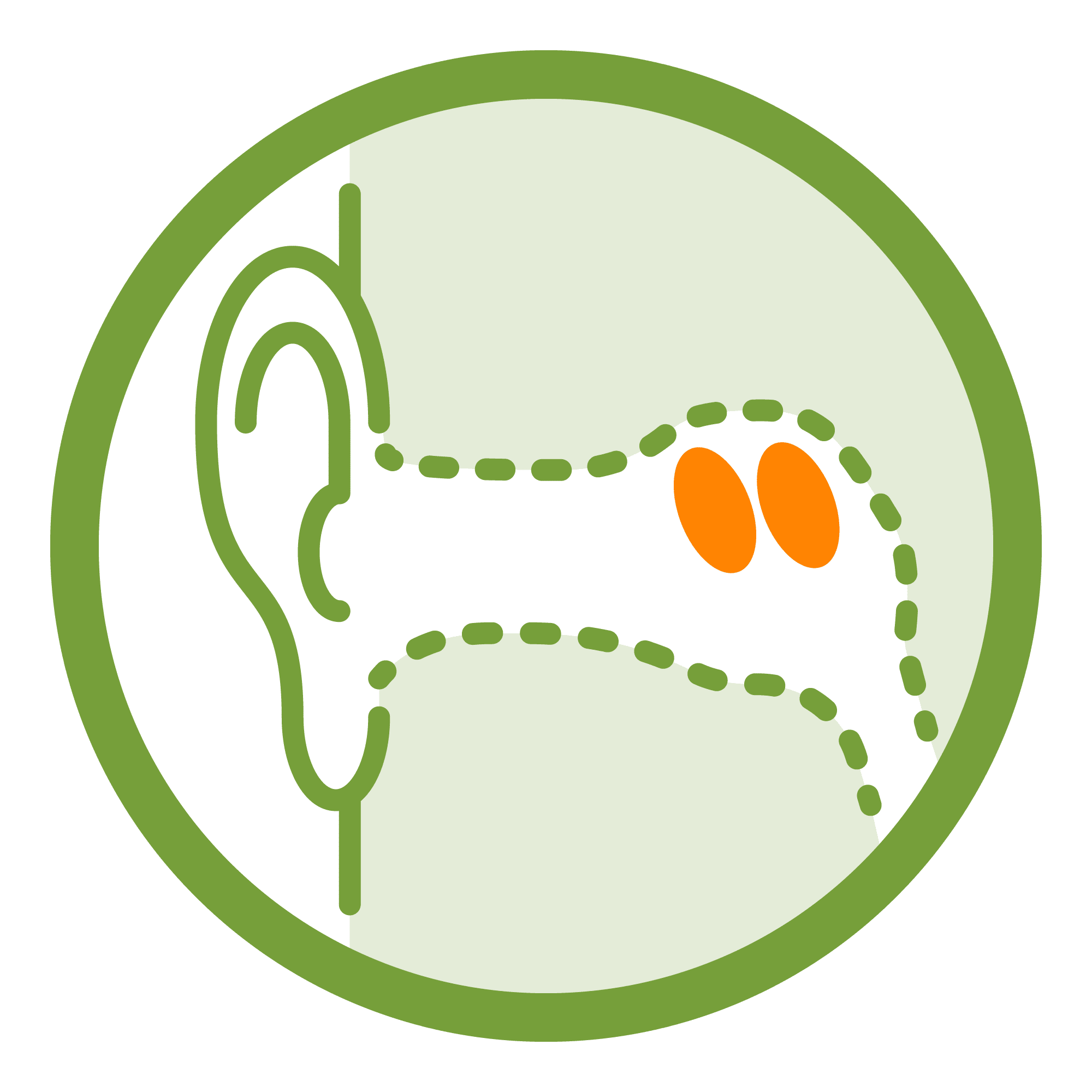
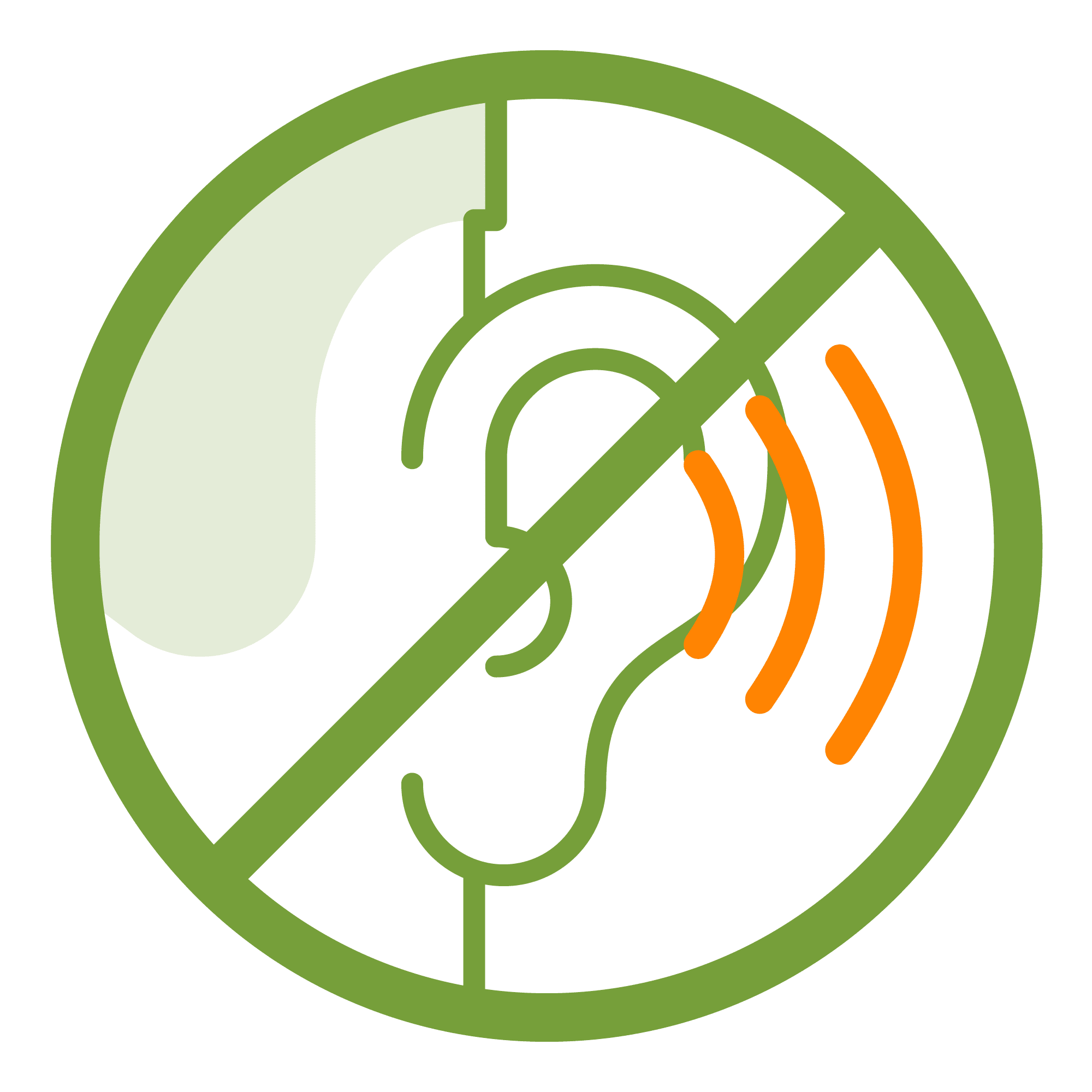


Hearing Loss
A person is said to have hearing loss if they are not able to hear as well as someone with normal hearing, meaning hearing thresholds of 20 decibels or better in both ears. Its severity can be mild, moderate, severe, or profound. Major causes include congenital or early onset childhood hearing loss, chronic middle ear infections, noise-induced hearing loss, age-related hearing loss, and certain medications that can damage the inner ear.
The impacts are broad and can be profound. They include delayed speech or language development, social isolation, loneliness, frustration, depression, poor academic performance, health sector cost, educational costs, loss of productivity and societal cost.
More information on hearing loss from the World Health Organization
Mastoid Abscess
A mastoid abscess is a puss-like material that collects within the middle ear and mastoid air cells (pockets of air in the middle ear). It may develop from an infection in the mastoid bone (the bone behind the ear) following inadequate treatment of middle ear infections. It can also occur from poor immunity or due to virulent bacterial infections. Complications include meningitis, brain abscess, sigmoid sinus thrombosis and facial nerve palsy. It requires emergency medical as well surgical treatment.
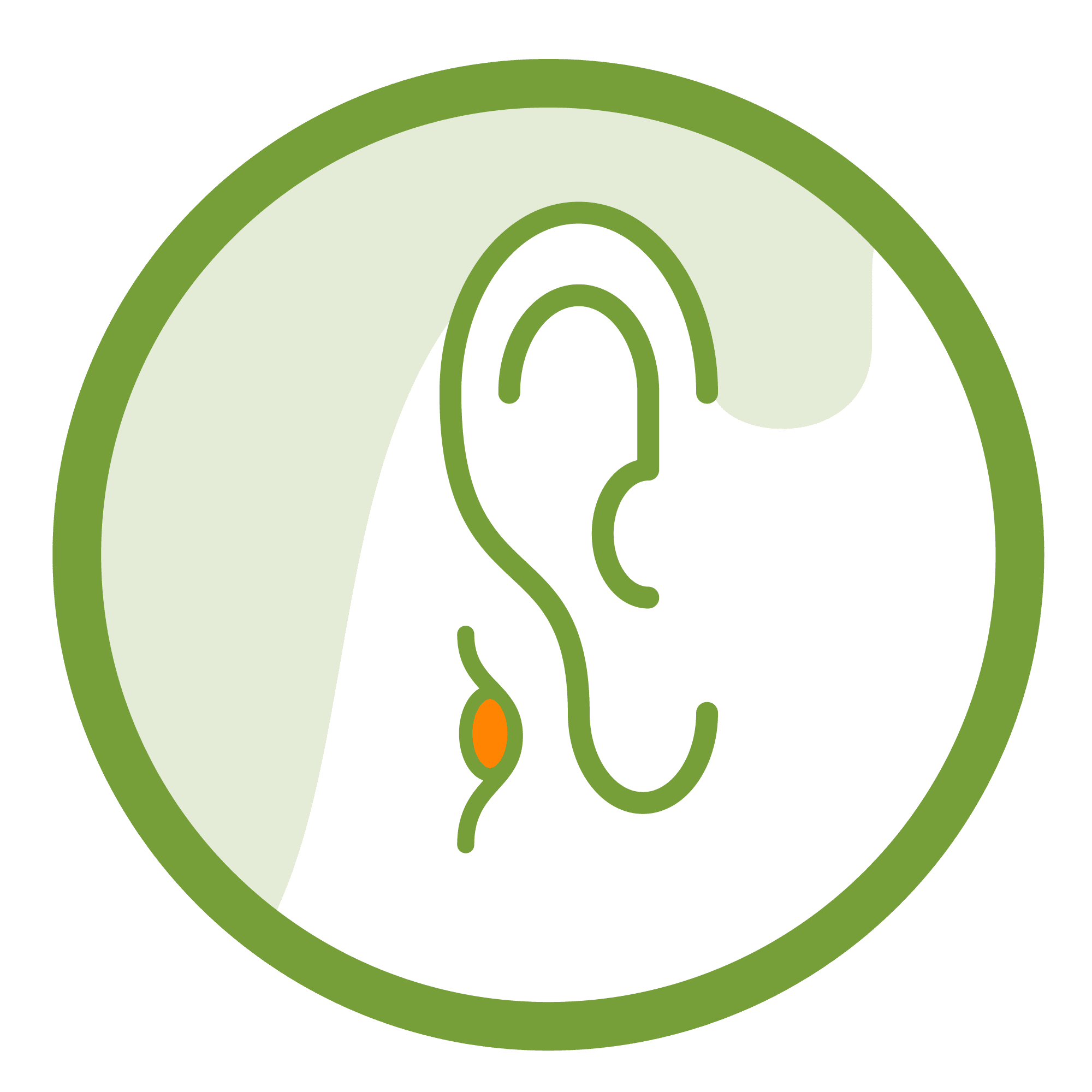


Mastoid Fistula and Cholesteatoma
A cholesteatoma is defined as a type of cyst located in the middle ear or the mastoid bone, which is behind the ear. If left untreated, it can damage the surrounding bones and tissues. Cutaneous mastoid fistula is the opening of mastoid air cells to the external environment due to erosion of the cortex of the mastoid bone following chronic mastoid infection, mastoid abscess and cholesteatoma. Cholesteatoma and mastoid fistula are primarily treated with surgery.
Neck Masses and Cysts
Congenital, developmental, and inflammatory lesions make up most of the head and neck masses seen in children. A practical approach to head and neck masses in children aims to differentiate whether masses are congenital (meaning present at birth), inflammatory, or the result of abnormal cells based on the location of the mass.


Nasal Polyp
Nasal polyps are soft, painless, grape-like, non-cancerous growths lining the nose or sinuses. Presenting symptoms include nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, and voice change (Hyponasality). Some causes include allergies, asthma, sinusitis, aspirin intolerance, and cystic fibrosis, to name a few. Treatment is provided by a combination of endoscopic sinus surgery and medical therapy.
Tonsillar Disease
Tonsillar diseases include acute tonsillitis, chronic and recurrent tonsillitis, bacterial infections of the tonsils, and abscesses. Tonsillitis can be caused by viral as well as bacterial infections. Viral tonsillitis is usually preceded by flu-like symptoms and does not need antibiotic therapy. However, bacterial tonsillitis requires antibiotic therapy. Tonsillar disease can result in swollen tonsils, leading to sleep disordered breathing and obstructive sleep apnea. Obstructive sleep apnea is an absolute indication for surgical treatment.
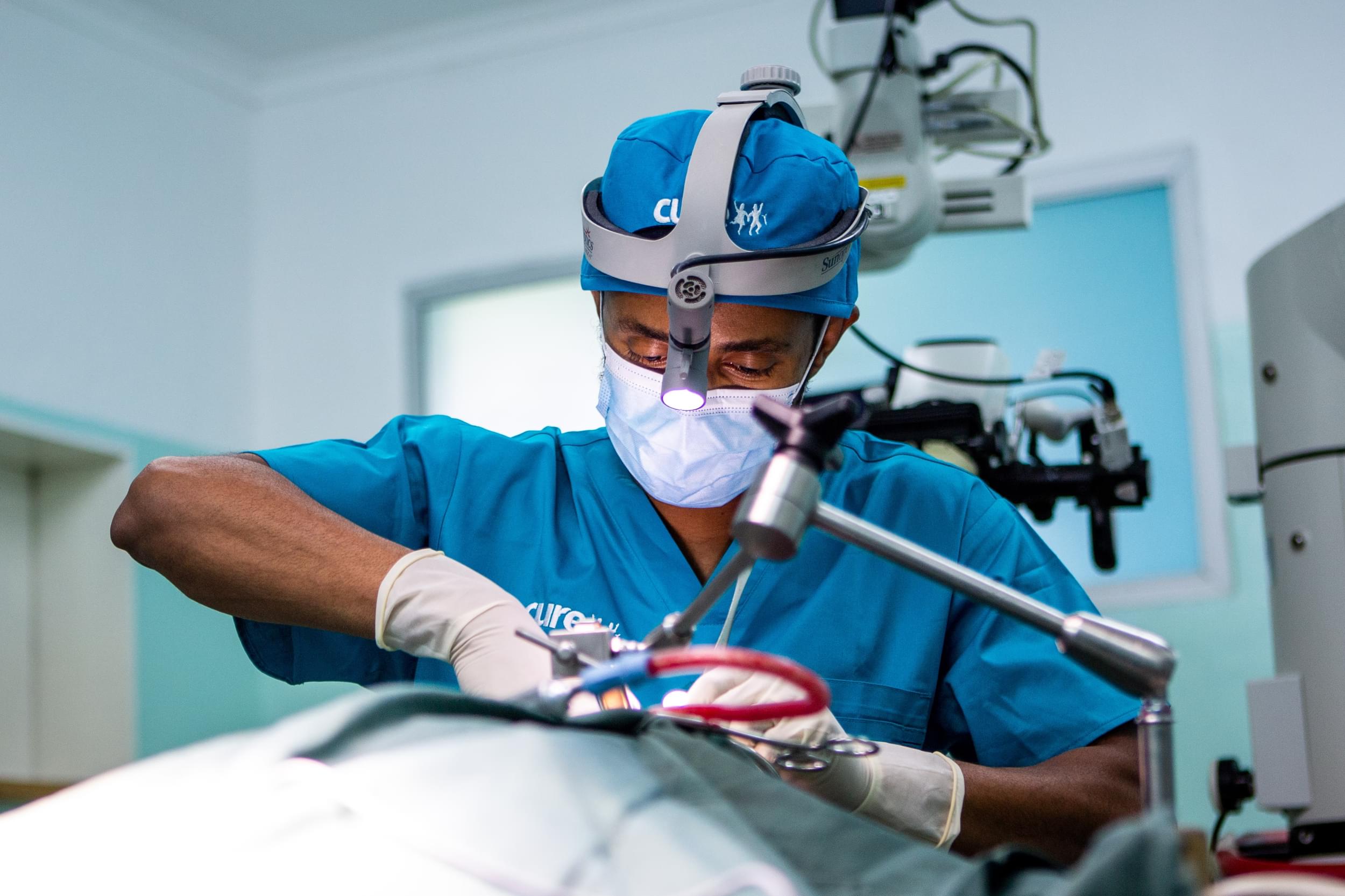
Children receive care every day at Beit CURE Children’s Hospital of Zambia
HOW PATRICIA WAS HELPED




